
STD Rates by State: Where Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Are Highest and Lowest
Last updated October 4, 2023.
Table of contents
- States With the Highest STI Rates
- Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis: Common STIs
- Chlamydia Statistics by State
- Gonorrhea Statistics by State
- Syphilis Statistics by State
- Ways to Lower Your Risk of STDs/STIs
- Related Content
Sexually transmitted diseases and infections (STDs/STIs) are quite common, and at an all-time high in the United States. They are typically spread from one person to another through sexual contact and oftentimes individuals with STIs experience mild to no symptoms—which can be a challenge to diagnose and treat.
Untreated STIs pose a serious problem as they can lead to long-term health consequences for yourself or your partner, such as female and male infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and cervical cancer (female).
As the number of STI cases continues to rise across the U.S., we decided to take a look at STI rates by state, using the CDC’s STD surveillance report to discover which regions have the highest rates.
Read on or skip to our infographic as we uncover rates of the most common STIs by state, and how both men and women can reduce their risk of STIs if they’re sexually active.
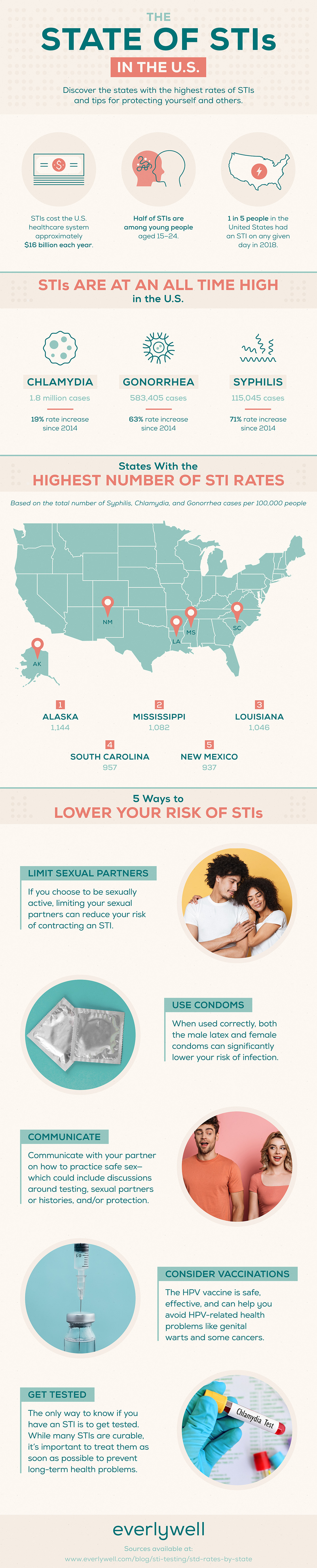
States With the Highest STI Rates
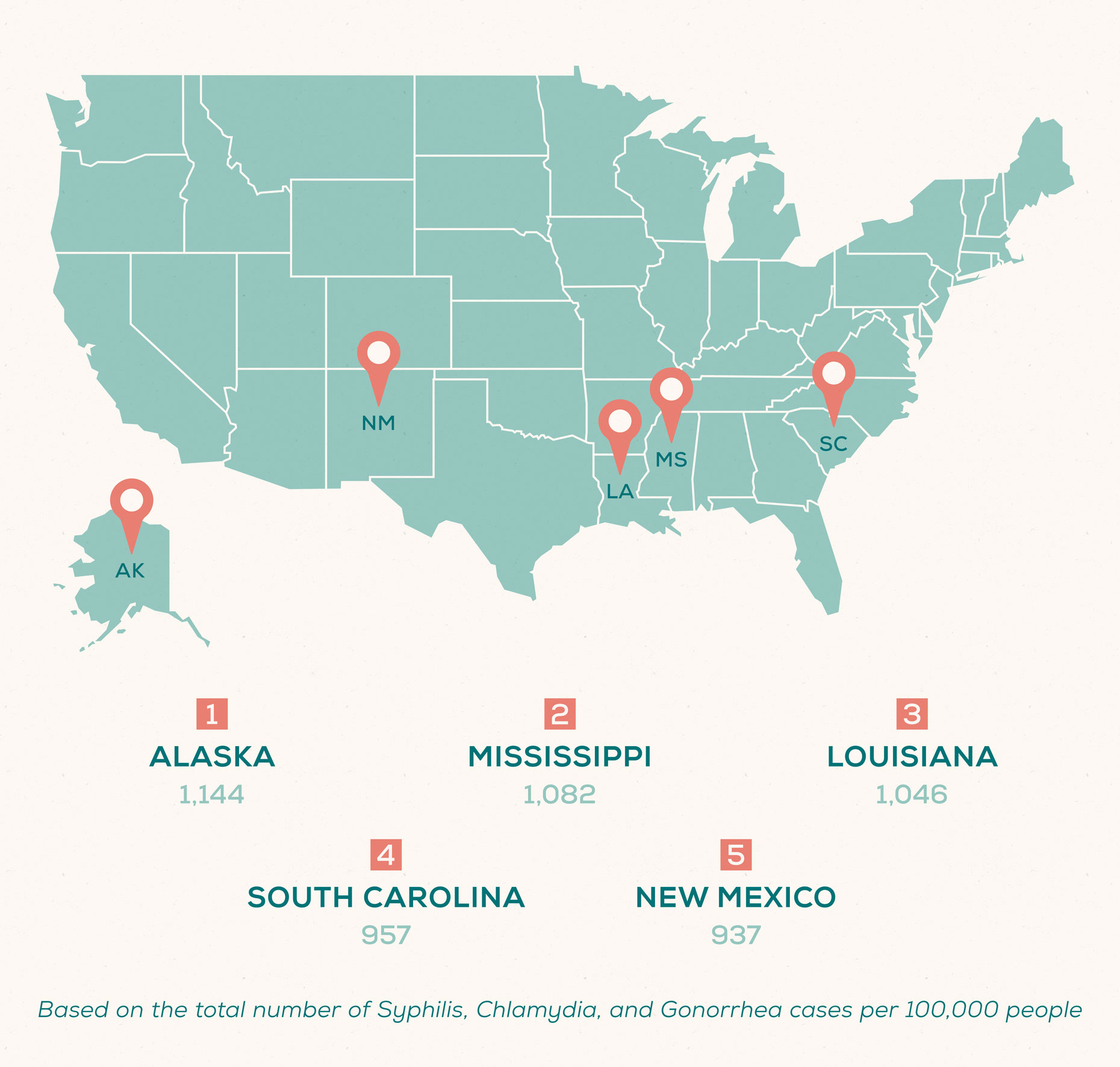
Based on total STI rates reported (for primary and secondary syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea only), the following states have the highest rates of sexually transmitted infections in the United States.
States with the highest STI rates (per 100,000 people):
- Alaska: 1,144
- Mississippi: 1,082
- Louisiana: 1,046
- South Carolina: 957
- New Mexico: 937
Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis: Common STIs
There are more than 20 different types of STDs/STIs. We cover some of the most common ones below.
Chlamydia
This is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection that's caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. Reported cases of chlamydia are about twice as high in females than in males and are highest among females 15–24 years of age. Once detected, chlamydia can be cured with proper antibiotic treatment.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an STI caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. Reported cases among males and females are equally common and reports of cases are high among individuals who are 15-24 years of age. Once detected, gonorrhea can be cured with proper antibiotic treatment.
Note that you can take an at-home chlamydia and gonorrhea test to check for these bacterial STIs from the convenience and privacy of home.
Primary and Secondary Syphilis
This STI is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. When a person contracts syphilis, they will generally develop a sore or sores on the infection site—this stage of infection is called “primary syphilis.” If left untreated, the infection may develop into “secondary syphilis,” which can cause a skin rash or sores on the mouth, vagina, or anus.
Syphilis can be cured with proper antibiotic treatment. However, treatment cannot undo damage that the infection has already caused, which is why it is important to detect and treat syphilis in its early stages. It’s possible to check for syphilis with an at-home syphilis test.
Chlamydia Statistics by State
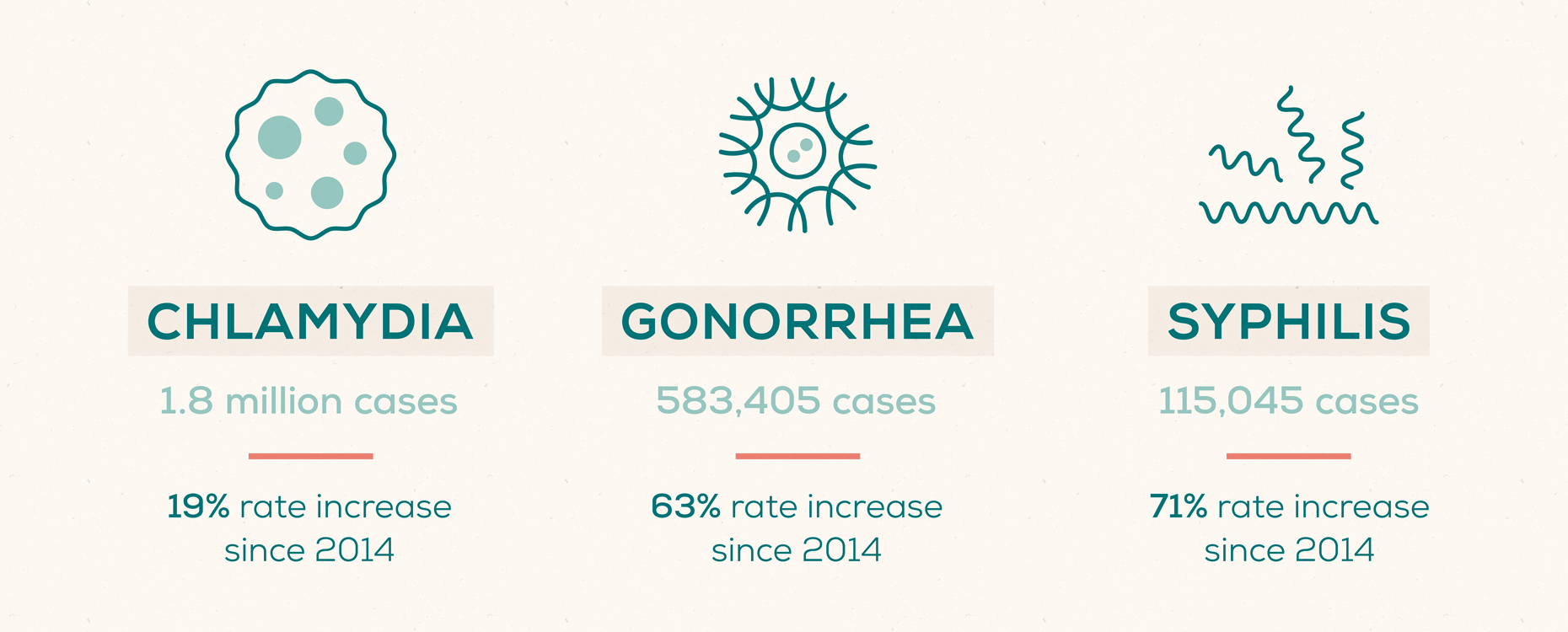
Among the STIs listed above, chlamydia is the most common. In 2018, there were 1.8 million cases of chlamydia reported in the United States—more than twice the amount of reported cases of gonorrhea and syphilis combined.
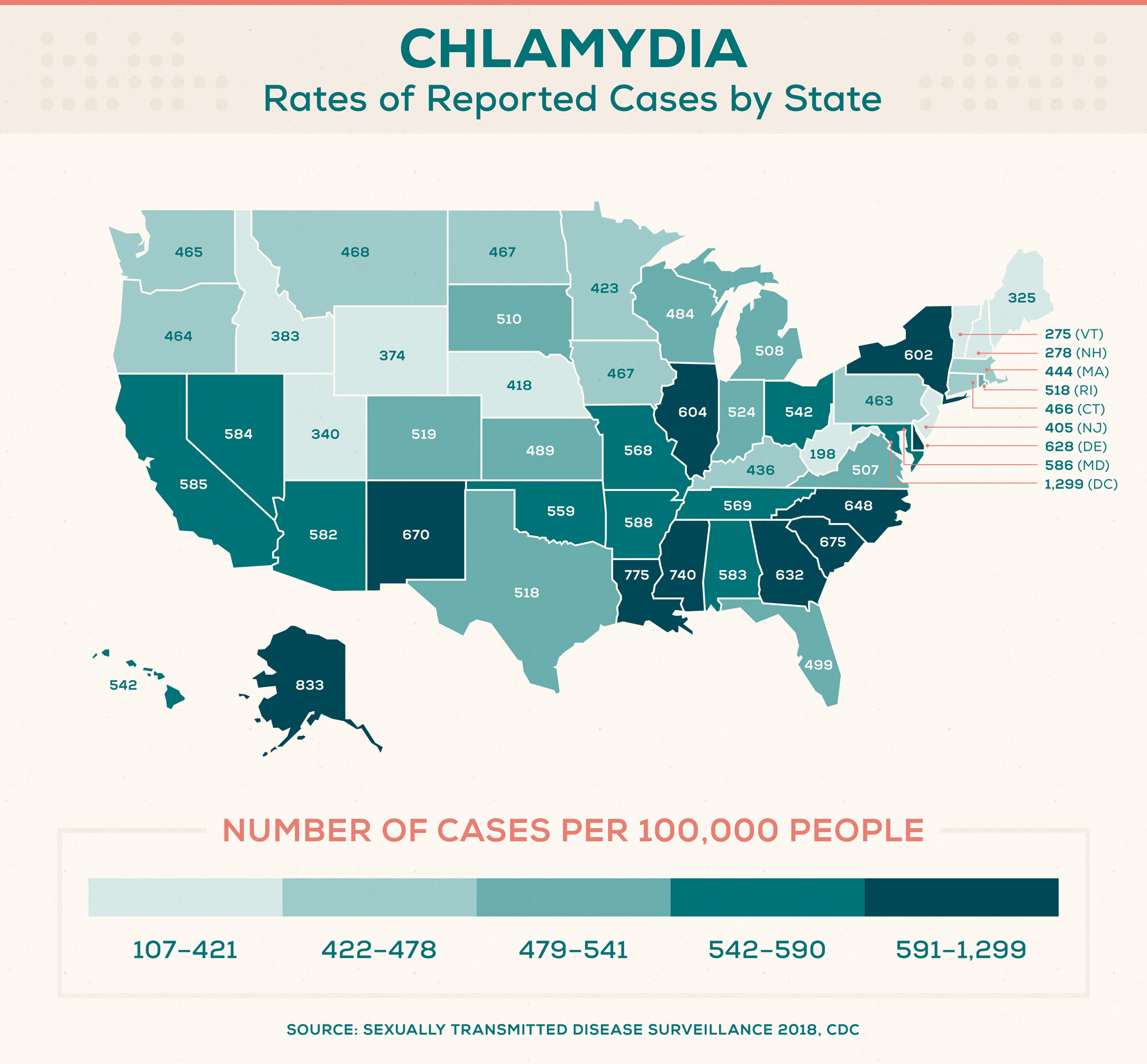
States with the highest rates of reported chlamydia cases (per 100,000 people):
- Alaska: 832.5
- Louisiana: 774.8
- Mississippi: 740.1
- South Carolina: 674.9
- New Mexico: 670.5
States with the lowest rates of reported chlamydia cases (per 100,000 people):
- West Virginia: 198.2
- Vermont: 274.5
- New Hampshire: 278.1
- Maine: 325.2
- Utah: 339.8
Gonorrhea Statistics by State
In 2018, there were 583,405 reported cases of gonorrhea—a 63% increase in reported cases since 2014. Similar to chlamydia, this infection affects both men and women and can cause health complications if left untreated.
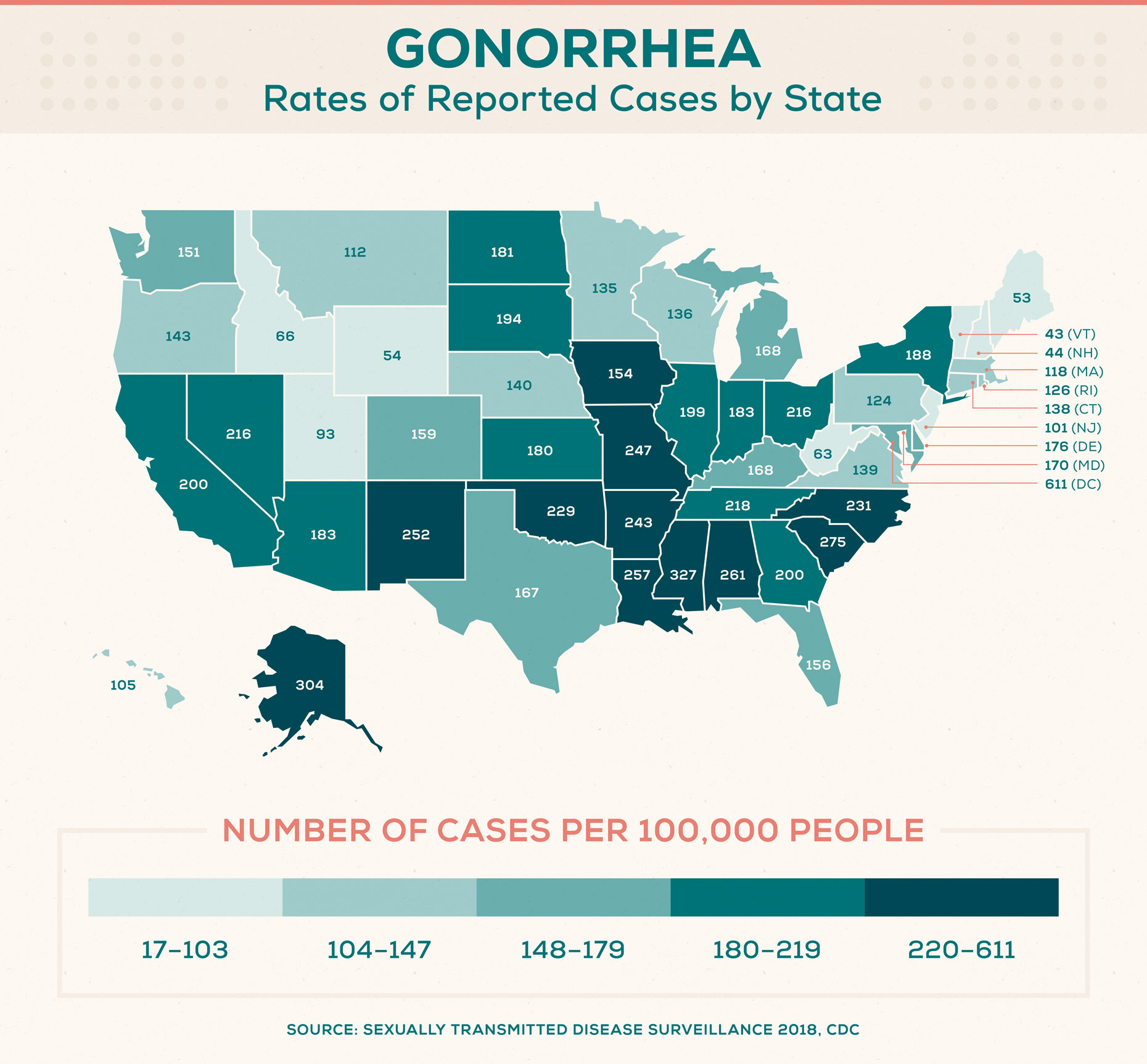
States with the highest rates of reported gonorrhea cases (per 100,000 people):
- Mississippi: 326.7
- Alaska: 303.7
- South Carolina: 274.7
- Alabama: 261.4
- Louisiana: 257.1
States with the lowest rates of reported gonorrhea cases (per 100,000 people):
- Vermont: 43
- New Hampshire: 44.2
- Maine: 53.1
- Wyoming: 53.7
- West Virginia: 62.9
Syphilis Statistics by State
Syphilis cases continue to be on the rise. In 2018, there were over 115,000 syphilis cases in the United States, which includes 35,000 newly reported cases of primary and secondary syphilis—the two earliest, most infectious stages. This is the highest reported number in nearly 30 years.
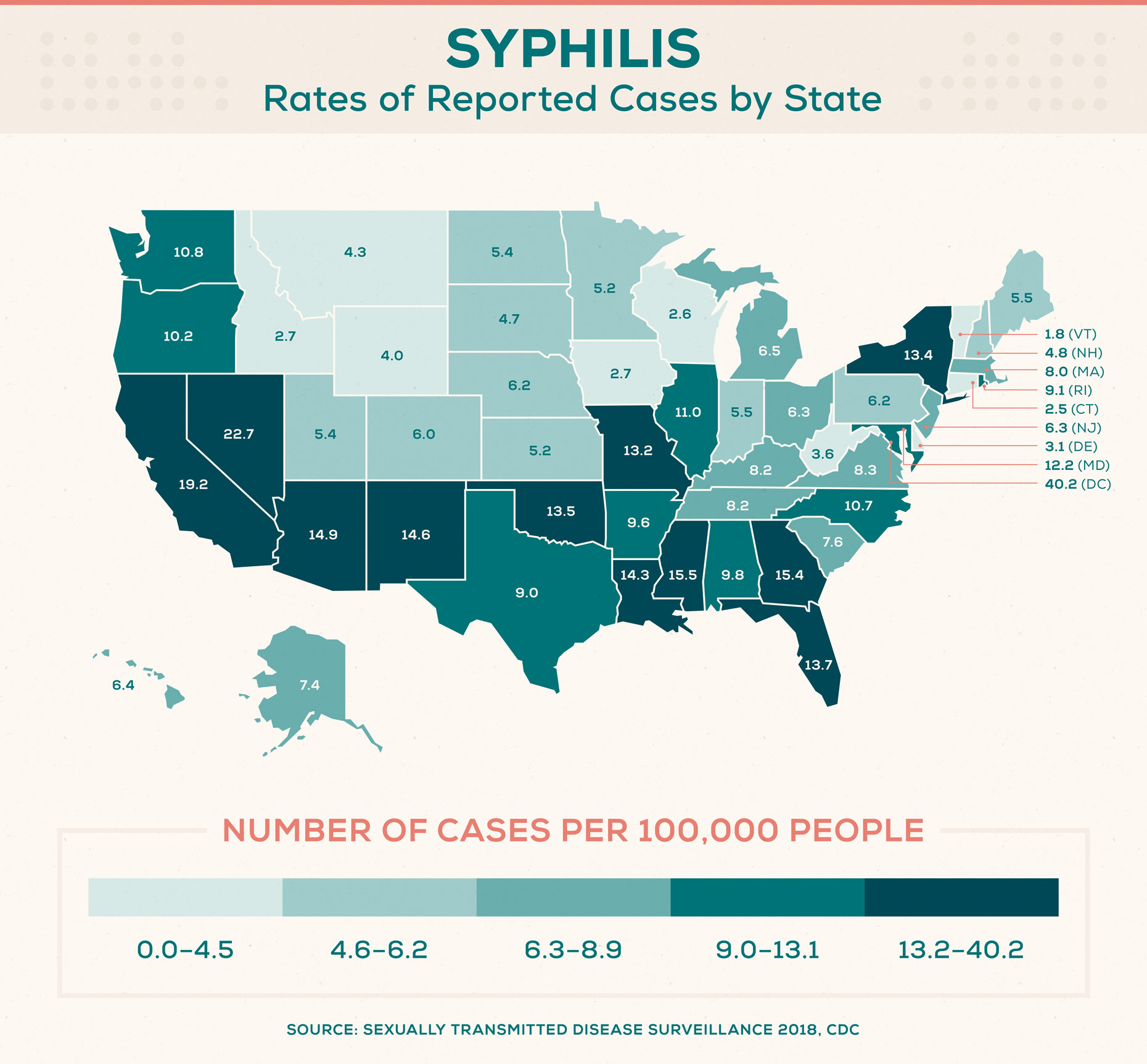
States with the highest rates of primary and secondary syphilis cases (per 100,000 people):
- Nevada: 22.7
- California: 19.2
- Mississippi: 15.5
- Georgia: 15.4
- Arizona: 14.9
States with the lowest rates of reported primary and secondary syphilis rates (per 100,000 people):
- Vermont: 1.8
- Connecticut: 2.5
- Wisconsin: 2.6
- Idaho: 2.7
- Iowa: 2.7
Ways to Lower Your Risk of STDs/STIs
When planning to be sexually active with a new partner, follow the tips below to help limit your risk of contracting an STD/STI.Use Condoms
When used correctly, both male latex and female condoms are effective in stopping most STDs/STIs from being passed from an infected sexual partner to another. To limit transmission of infection, condoms can be used each time a person has oral, vaginal, or anal sex.
Communicate With Your Partner
To protect yourself and your partner from STDs/STIs, it’s important to communicate and talk about safe sex before being intimate for the first time. Here are several questions you can ask to get the conversation started:
- “Is it okay if we talk about a few things before we have sex?”
- “When was the last time you were tested for STIs?”
- “How are we going to practice safe sex?”
- “Are you okay with using condoms to prevent pregnancy and STIs?”
Get Tested
It’s best for both you and your sexual partner to get tested for STIs before you are intimate. Remember, many people who have an STI will not experience any symptoms, and may not even know that they have one. That’s why getting tested and potentially treating your STI is an effective way to protect yourself and others.
If you’re planning to be sexually active with someone for the first time or you’re experiencing symptoms characteristic of an STI, consider taking an STD test kit for men or women at home for convenient and discreet results.
Consider Vaccinations
Currently, there are vaccines available to protect uninfected individuals against HPV (human papillomavirus) and hepatitis B. Discussing your vaccination options with your primary care provider is the best way to help you determine whether you may benefit from vaccination.
STIs/STDs are among the most common infections across the United States, and anyone who’s sexually active can contract or spread them. If you’re planning to be sexually active with a new partner, get tested and use protection to ensure you keep yourself and others safe from harmful or even life-threatening infections.
Related Content
38 STD and STI Statistics for College Students: How To Keep Yourself Healthy and Safe
Sexual Health During and After the Pandemic: High Rates of STIs
STDs in Older Adults: Everything You Need to Know as You Age
References
Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2021. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm. Accessed March 15, 2021.
